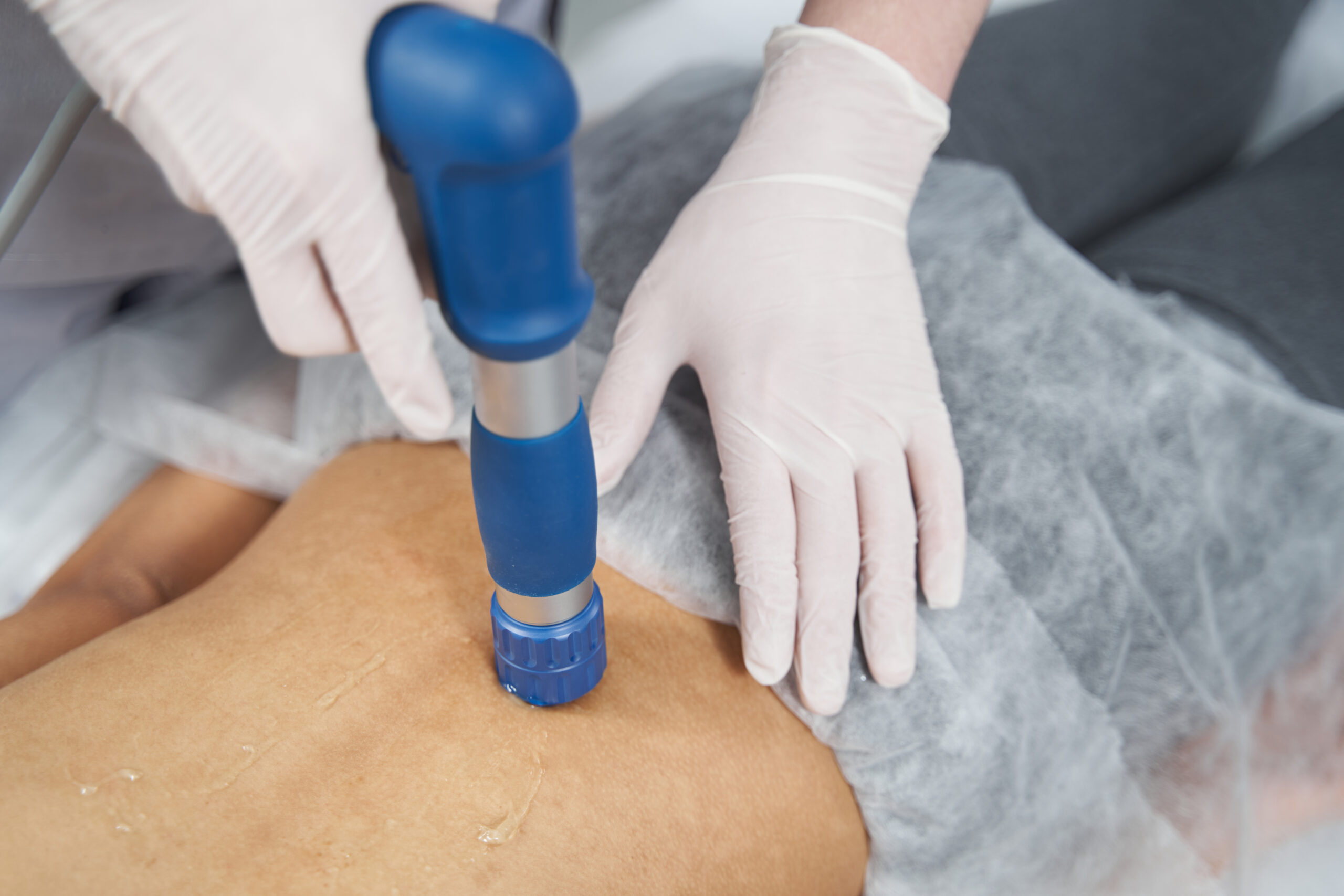
Shockwave therapy has gained significant traction as a noninvasive treatment for musculoskeletal conditions, chronic pain, and tendon-related injuries. While many patients report noticeable improvements, it’s natural to wonder: can shockwave therapy cause damage? This question is worth examining, especially for those considering the treatment or recommending it to others.
What Is Shockwave Therapy and How Does It Work?
Shockwave therapy uses acoustic waves to deliver energy to specific areas of the body, stimulating healing responses in tissue. It’s commonly used for conditions like plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, calcific shoulder tendinopathy, and Achilles tendinopathy. There are two main types—focused and radial—each varying in depth and intensity.
The treatment promotes cellular regeneration, increases blood flow, and breaks down calcified tissues, helping the body recover more efficiently. Despite these benefits, questions remain about its safety and any potential for tissue harm.
Can Shockwave Therapy Cause Damage?
The short answer: serious damage from shockwave therapy is rare, especially when administered correctly by trained professionals. However, like any medical treatment, it is not entirely without risks.
Most concerns about damage stem from:
- Incorrect application or settings (e.g., using energy levels that are too high)
- Pre-existing conditions that contraindicate treatment (e.g., bleeding disorders or malignancies)
- Lack of screening for areas near sensitive anatomical structures
When these risk factors are accounted for, adverse outcomes are uncommon. The vast majority of patients experience only minor, temporary side effects.
Common Side Effects Versus Actual Damage
To clarify, the term “damage” is often confused with common side effects, which include:
- Mild swelling
- Redness
- Local discomfort during or after treatment
- Bruising
These effects are not indicative of harm but rather normal responses as the body begins to heal. They typically subside within a few days and do not require medical intervention.
Severe complications, such as tendon rupture or nerve damage, are extremely rare and usually linked to predisposing factors rather than the therapy itself.
Who Should Avoid Shockwave Therapy?
Though generally safe, shockwave therapy may not be suitable for everyone. The following groups should consult their healthcare provider before proceeding:
- Individuals with coagulation disorders or on anticoagulants
- Patients with tumors near the treatment site
- Pregnant individuals (especially over the pelvic region)
- People with infections or open wounds in the treatment area
- Patients with severe sensory or circulatory neuropathies
Proper patient screening and adherence to protocols are key in preventing unintended effects.
Ensuring Safe and Effective Use
To minimize risks and avoid potential damage, consider the following:
- Choose a qualified provider with experience in administering shockwave therapy
- Ask questions about the device type, treatment frequency, and intensity settings
- Report any unusual symptoms immediately to your provider
- Follow post-treatment instructions to allow for optimal healing
When performed properly, shockwave therapy remains a trusted and scientifically supported treatment modality.
Conclusion
So, can shockwave therapy cause damage? While the possibility exists under inappropriate conditions, the risk is minimal when guided by trained hands and proper patient selection. Understanding how the therapy works and what to expect can provide reassurance and help you make an informed decision about whether it’s the right option for your recovery.